One of the first questions we ask customers as we learn more about their application is, “Are you dealing with pipe or tube?” Even those who have years of experience in the industry use the terms interchangeably, however, there is variation between the two when it comes to size, nomenclature and even shape. It is important to know the difference between pipe and tube to learn more about your application. Having this knowledge should allow you to purchase or rent the right tools and equipment.
.jpg?width=501&name=pipe-vs-tube%20(2).jpg)
What Industries Use Pipe & Tube
Common pipe and tube industries:
- Aerospace – Tube
- Brewery/Distillery - Both
- Food/Dairy/Beverage - Tube
- Chemical/Petrochemical - Both
- Pharmaceutical/Biopharmaceutical - Tube
- Power Generation – Both
- Pulp/Paper - Both
- Oil/Gas – Pipe
- Semiconductor - Tube
- Shipbuilding - Both
- Wastewater Treatment – Pipe
Measuring Pipe vs Tube
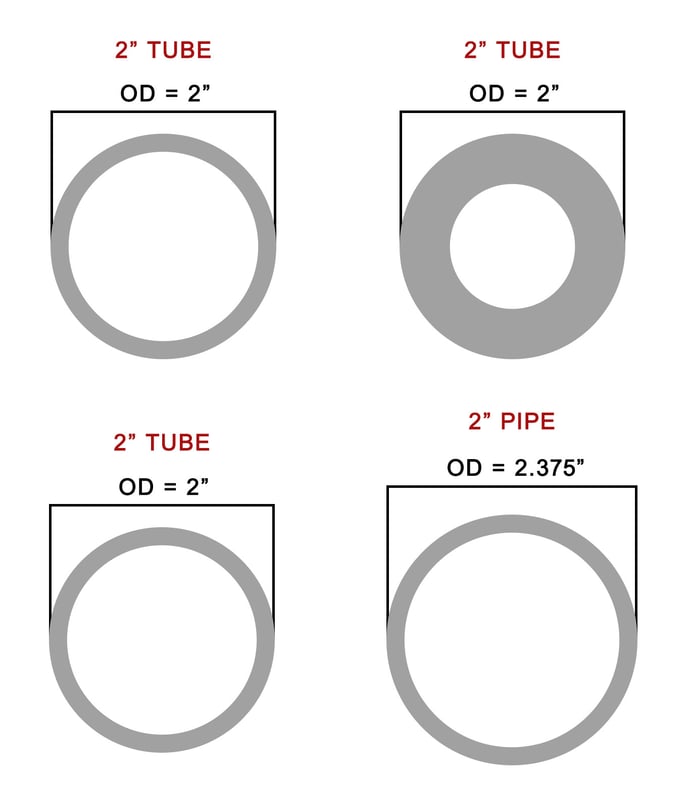
Though there are many differences between tube and pipe, the most significant difference is found in the size and way they are measured. Tube is measured by outside diameter (OD) and wall thickness. Because tube is used in structural applications, OD is the most important dimension to consider. The OD is measured in actual sizes. Simply if you are using 2” tube – your piece of tube measures 2” across from the outside of the tube to the other side. As the inside diameter (ID) changes the outside diameter stays the same.
Now, here is when it gets tricky. Pipe is measured in Nominal Pipe Sizes (NPS), inside diameter and schedule (wall thickness). The actual OD for pipe can be calculated from the equation:
OD = ID + 2 * Wall Thickness
Let us compare 2” Tube and 2” Pipe. As you can see below, a piece of 2” tube has the same 2” OD no matter the wall thickness. When it comes to pipe, the actual OD is 2.375” even if the wall thickness is the same as the 2” Tube.
When it comes to pipe, referencing a pipe chart like the one below can help you quickly find the measurements you need.
| Pipe Size | Schedule | Wall | ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8" | 10S | 0.049 | 0.307 |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.068 | 0.269 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.095 | 0.215 | |
| 1/4" | 10S | 0.065 | 0.41 |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.088 | 0.364 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.119 | 0.302 | |
| 3/8" | 10S | 0.065 | 0.545 |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.091 | 0.493 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.126 | 0.423 | |
| 1/2" | 5S | 0.065 | 0.71 |
| 10S | 0.083 | 0.674 | |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.109 | 0.622 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.147 | 0.546 | |
| 160 | 0.188 | 0.464 | |
| XX | 0.294 | 0.252 | |
| 1" | 5S | 0.065 | 1.185 |
| 10S | 0.109 | 1.097 | |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.133 | 1.049 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.179 | 0.957 | |
| 160 | 0.25 | 0.815 | |
| XX | 0.358 | 0.599 | |
| 1 1/4" | 5S | 0.065 | 1.53 |
| 10S | 0.109 | 1.442 | |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.14 | 1.38 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.191 | 1.278 | |
| 160 | 0.25 | 1.16 | |
| XX | 0.382 | 0.896 | |
| 1 1/2" | 5S | 0.065 | 1.77 |
| 10S | 0.109 | 1.682 | |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.145 | 1.61 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.2 | 1.5 | |
| 160 | 0.281 | 1.338 | |
| XX | 0.4 | 1.1 | |
| 2" | 5S | 0.065 | 2.245 |
| 10S | 0.109 | 2.157 | |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.154 | 2.067 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.218 | 1.939 | |
| 160 | 0.344 | 1.687 | |
| XX | 0.436 | 1.503 | |
| 2 1/2" | 5S | 0.083 | 2.709 |
| 10S | 0.12 | 2.635 | |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.203 | 2.469 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.276 | 2.323 | |
| 160 | 0.375 | 2.125 | |
| XX | 0.552 | 1.771 | |
| 3" | 5S | 0.083 | 3.334 |
| 10S | 0.12 | 3.26 | |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.216 | 3.068 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.3 | 2.9 | |
| 160 | 0.438 | 2.624 | |
| XX | 0.6 | 2.3 | |
| 3 1/2" | 5S | 0.083 | 3.834 |
| 10,10S | 0.12 | 3.76 | |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.226 | 3.548 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.318 | 3.364 | |
| XX | 0.636 | 2.728 | |
| 4" | 5S | 0.083 | 4.334 |
| 10, 10S | 0.12 | 4.26 | |
| 40ST, 40S | 0.237 | 4.026 | |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.337 | 3.826 | |
| 120 | 0.438 | 3.624 | |
| 160 | 0.531 | 3.438 | |
| XX | 0.674 | 3.152 | |
| 4 1/2" | 40ST, 40S | 0.247 | 4.506 |
| 80XS, 80S | 0.355 | 4.29 | |
| XX | 0.71 | 3.58 |
Other Differences Between Tube & Pipe
Shape
Pipe is always round while tube can vary in shape. While the tube we work with in the orbital welding industry is always round, there is also square and rectangular tube.
Tolerances
Pipe has a looser tolerance than tube, especially in larger OD sizes. This includes: Diameter Tolerance, Wall Thickness/Weight Tolerance, Straightness Tolerance, Roundness (Ovality) Tolerance.
Orbital Tube Welding vs Orbital Pipe Welding
Most tube sizes and small pipe can be welded through the fusion process. This type of orbital welding is done with enclosed weld heads. The process fuses existing material and creates a clean, sanitary weld optimal for critical industries that process items that cannot risk contamination, such as food and pharmaceuticals. Fit up is critical for this type of weld and requires the proper cutting and tube facing tools.
Large orbital pipe welding is performed with open face style weld heads and added filler wire. Due to heavy pipe walls, a bevel is necessary - otherwise, there would not be full penetration during the weld. Filler wire replaces the metal that was removed during the bevel. This usually calls for multiple orbits or “passes” around the pipe seam. Lose tolerances on pipe can be combated with tracking rollers and AGC – stay tuned for our next blog with more details on this process.
It is important to communicate the details of your tube and pipe application with your purchasers and key decision-makers so that they are informed when purchasing equipment. With the right information, Morgan Industrial Technology can find the right solution.

Jun 12, 2020 12:00:00 AM

-1.png?width=520&height=294&name=Blog%20Featured%20Image%20(1)-1.png)
.png)
Comments